What is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)?
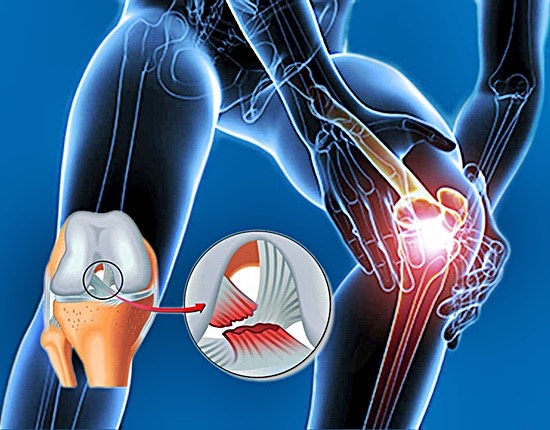
And ligament It is a band of very resistant and elastic connective tissue whose function is the union of the bones within a joint. Specifically, the stability of the knee is fixed by four ligaments: anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial lateral ligament (LLL), and medial lateral ligament (LLL).
From the anatomical point of view, the cruciate ligaments follow the following route:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL): Extends from the medial aspect of the lateral condyle of the femur to the anterior intercondylar area of the tibia. Its function is to prevent the anterior displacement of the tibia with respect to the femur. It is in this ligament where most injuries occur.
- Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL): Extends from the lateral face of the medial condyle of the femur to the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia. Its function is to stabilize the posterior sliding of the tibia with respect to the femur.
Depending on the degree of injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, they can be classified into three types:
- Grade I sprain: The ligament has been slightly damaged, causing pain, edema and slight inflammation, null or slight functional impotence.
- Grade II sprain: Partial tear of the ligament, pain, edema and inflammation is greater, moderate functional impotence.
- Grade III sprain: Tear or complete rupture, pain, edema and inflammation are very intense, total functional impotence and great instability of the knee.
Causes of anterior cruciate ligament injury
Most of the ACL injuries They occur in those sports practices that require turns of the lower body and braking:
- Quickly change direction.
- Hyperextension with sudden rotation of the knee (rotate the knee with the ankle and foot firmly planted on the ground).
- stop suddenly
- Direct trauma (direct contact or collision) to the posterior part of the tibia
- Combination of knee valgus (knee in) and external rotation.
- Combination of knee varus (knee out) and internal rotation.
- Landing incorrectly.
- Slow down the movement.
On the other hand, it is also important to highlight a series of risk factor's that can increase the probability of suffering this injury:
- Play sports such as soccer, basketball, alpine skiing, American football, etc.
- Being a woman: due to her greater joint laxity (among others).
- Being in poor physical shape.
- Excess valgus knee.
- Play sports on uneven terrain.
- Wearing inappropriate or oversized footwear.
Symptoms of anterior cruciate ligament tear
There are several pathologies with symptoms similar to those mentioned above when you injure the LCA (intense pain, inflammation, edema, instability, discomfort when walking, etc.). To differentiate them, they must be done a series of tests:
drawer test
The injured person should be placed in a supine position (face up) with the hip flexed to 45° and the knee flexed to 90°. With the foot fixed in neutral rotation, a health personnel (physician, physiotherapist, etc.) performs anterior traction on the tibia. If a soft top appears, there was an ACL injury.
Bone scan
This test specifically will not clearly show the ACL lesion, but it will show if it is associated with a bone lesion.
Resonance
This is one of the best tests to determine the degree of ACL injury since it creates better images of the soft tissues.
Treatment of anterior cruciate ligament rupture
Treatment of the knee in case of ACL injury will vary depending on whether conservative, that is, the affected person will not go through the operating room for recovery, or if it is surgical. In general, the majority of grade II and III tears usually opt for this form of treatment and more so if we are talking about athletes.
non-surgical treatment
In case of conservative treatment it is recommended strengthen the hamstrings (which can be worked on in an open kinetic chain) and strengthening of the quadriceps, taking into account that the load must be proximal so as not to favor the anterior drawer. All these types of exercises must be prescribed by health personnel (physiotherapist or doctor).
surgical treatment
Regarding a surgical treatment, it must be taken into account that the treatment used is the ligamentoplastia, thus reconstructing the ligament, being able to use various materials:
- Autograft (tendon repair): It is the most used method. To do this, fibers are taken from the patellar tendon or from the patient's own goosefoot tendon.
- Aloinjertos: the tendon to perform the ligamentoplasty belongs to a cadaver.
- Prosthesis.
Once the surgery has been performed and medical discharge has been received, the injured person must follow a strict rehabilitation at the hands of a physiotherapist where he will carry out different techniques for the optimal recovery of the knee.
Among these techniques, the presotherapy. During the first days it would be advisable to use mode 2 of our machine SIZEN, which is indicated to drain excess fluid accumulated in the knee after the operation.
Once the patient gradually returns to sports activity, he may feel muscle overload due to lack of sports habit, for which mode 3 or 4 is more recommended, with which the athlete will obtain rapid muscle recovery.
How to prevent anterior cruciate ligament injury?
Finally, we are going to give you a series of tips so that you can prevent, as far as possible, anterior cruciate ligament injury, thus avoiding long months of sports break:
- Strengthening the hamstrings, quadriceps and abdominal muscles.
- Strengthening of the external hip rotator muscles such as the gluteus medius, gluteus maximus and tensor fascia lata.
- Go periodically to the physiotherapist to avoid overloading the muscles mentioned above and so that they can perform their function correctly.
- Avoiding muscle fatigue using presotherapy SIZEN.
- Train the techniques of jumping, turning, braking and acceleration.
- Respect rest days.
- Perform the exercises with appropriate footwear.
Author
Alice Vicario, physiotherapist and creator of Fisiovik (IG: @fisiovik).
I have studied Sports Sciences and Physical Activity and I specialized in the branch of Health. I worked in a physiotherapy clinic for years as a sports rehabilitator until I finally decided to do physiotherapy.



Share:
Runner's Syndrome: What is it and how is it cured?
What happened to Alexia Putellas?